Table of Contents
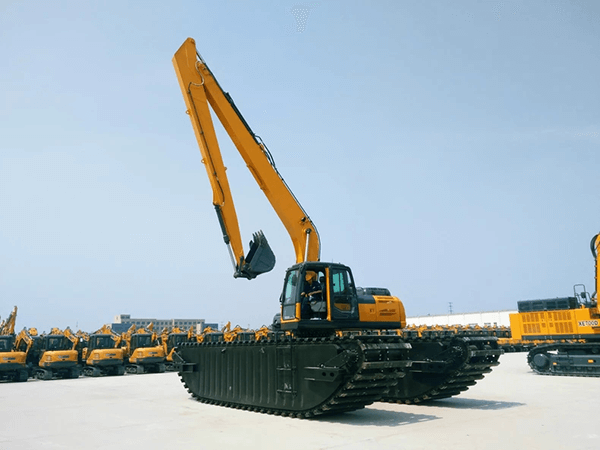
An amphibious excavator is a type of excavator that features sealed pontoon equipment that allows it to perform dredging work while floating in shallow water. The pontoons are built with high tensile strength steel, due to the working conditions they are in, they are resistant to corrosion and able to work in high salinity conditions as in the case of working with seawater. This ensures that the excavator can operate even in extreme conditions. It is equipment that is specifically designed to maneuver in swampy areas such as wetlands and soft ground, as well as to float on water. These excavators are fully self-propelled using a direct drive guide hydraulic system.
The physical principle that makes the amphibious excavator possible lies in the hermetically sealed pontoons, which are designed under the Archimedean principle. Coupled with its large footprint, this creates really low ground pressure. The machine is capable of operating within dry, soft, and boggy areas with little or no risk of being trapped in mud.
Undercarriages are considered as one of the main innovations in the area of the construction industry. These excavators are capable of operating in the harsh wetlands that are common throughout the world, especially in North America and Europe. Commonly, engineers were limited to conducting operations on solid ground, so under these conditions they would have to figure out how to generate solid ground for these machines by building roads or introducing barges through canals. Because these wetland-related overhead costs were required to be reduced, engineers developed the amphibious landing gear. The amphibious undercarriage could be installed on excavators and other heavy work equipment, adhering the undercarriage gives it buoyancy and the ability to work in wet environments without the need to build a solid base to transport it.

Amphibious equipment modifications are ideal for safely transporting workers and equipment to job sites on terrain that is too soft to walk and too dense to float. Before the use of amphibious excavators, developing industrial projects required workers to build canals, roads, or platforms before operating heavy equipment in swamps and marshes. This extra point for adapting the equipment to the working conditions was not only very extensive and difficult, but it was also very expensive and really harmful to the local environment because they were usually wetlands and swamps with a fragile ecology. On the other hand, these roads and channels were necessary to support loads of large machinery in soft or wet terrain, so sometimes they were not unnecessary work, but it was very limiting. Using amphibious excavators the procedure is much simpler, many steps can be eliminated by driving the machinery directly to the job site.
CHARACTERISTICS OF THE AMPHIBIOUS EXCAVATOR
The most notable feature of the amphibious undercarriagethat sets the equipment apart from a common excavator is the fact that it can provide buoyancy through hermetically sealed pontoons. The pontoons, which are extendable, allow the excavator to float in the water with the option of mounting vertical pallets if there is no different uneven terrain on which there is a risk of operation. The movement is carried out by means of the chain of chains that uses a multisynchronous hydraulic drive system. The track chain is used to support flotation, provides a higher level of traction efficiency and stability over a wider range for all types of operations, that is, according to ground conditions. The excavator can adapt with different attachments for each application. Due to this ability, it is possible for operators to perform a wide range of tasks for different industrial applications.
INDUSTRIAL APPLICATIONS
By common sense it is known that amphibious equipment will be useful to be used around wetlands and swamps, however, there are many other scenarios and conditions in which using amphibious equipment allows the job to be easier. The projects that are carried out around oceanic coasts, riverbeds and especially in areas of recent floods in which using an amphibious excavator is the best option to save costs and optimize operating time. Amphibious excavators can function efficiently in a wide range of applications, including flood and disaster recovery efforts, dredging, environmental remediation, and various construction projects such as pipeline, levee, or highway laying.
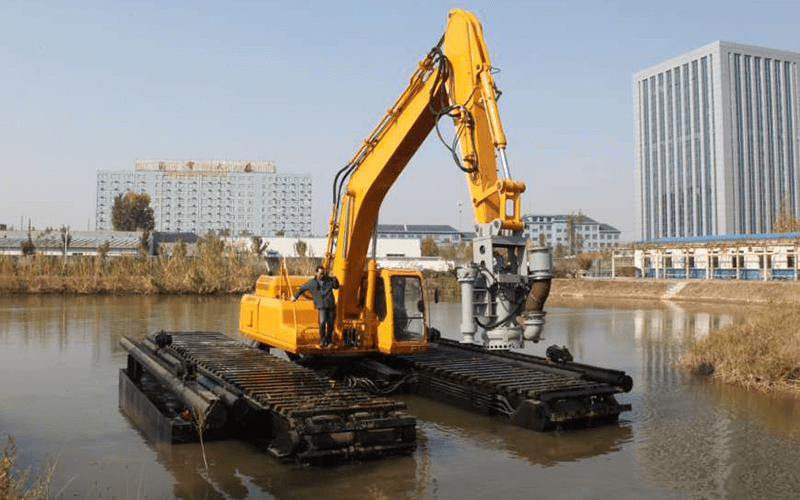
Using amphibious excavators is also the best option for environmental dredging, so its use is not only limited to the construction area. Dredging tasks are sometimes hampered by shallow water depths because excavators can easily get stuck or have limited reach. Due to the versatility of amphibious equipment that can float on water and can be handled on land, the operator does not have to worry about operating either too close or too far from the water’s edge. The wide tracks and a convenient weight for the operation mean that the pressure on the ground is not excessive, on the other hand, a much heavier equipment causes deep furrows. Additionally, the ability to mount a dredge pump directly to the excavator gives it the ability to have optimal movement and production rates.
BUILT TO PERFORM IN ANY SITUATION
EXCAVATION DREDGING AND SUCTION DREDGING
All types of excavation dredging in shallow water areas, which are considered up to 9 meters, should be done with an amphibious excavator. The removal of mud or stones, the transformation of warehouse spaces or the cleaning of industrial waste ponds are the most common applications, generally they are more used in environmental control aspects.
DREDGING OF INPUT CHANNELS AND RESERVOIR IN HYDROELECTRIC PLANT
The sediments that accumulate at the bottom of the inlet channels and the dam reservoir of the hydroelectric power plant can be dredged to maintain sufficient flow for the plant operations, and especially to take care of the internal equipment of hydroelectric power plants, it is a type of preventive maintenance.
CUT THE AQUATIC VEGETATION
Aquatic vegetation that grows at the bottom of the river or lake can be removed with an amphibious excavator and a rake. It is possible to also remove the roots of the plant and thus prevent the plants from growing again. If necessary, special hydraulic tools can be used to cut. As a complement, a conveyor belt and a cutter can be used, for some cases, especially for invasive plants.
CLEANING
It is simple to operate an amphibious excavator in canals and other narrow waterways. Trash, tree leaves and branches, and excess sediment that accumulates at the bottom of the canal can be removed by dredging.
MINING INDUSTRY
Using an amphibious excavator can be useful in many stages of open pit mines. It is often used, for example, to assist water pumps and other drainage and dam work.
UNDERCARRIAGE
The undercarriage is an essential part of understanding the operation of the amphibious excavator. It is a multi-equipment supporting structure, the amphibious hydraulic landing gear has to develop various supporting functions. In the case that it is equipped with a trencher, it will serve as an integral piece of equipment in controlling insects, especially mosquitoes, as well as digging trenches for laying pipes, for example. When using the amphibious hydraulic undercarriage, it can traverse swampy and wet terrain with partial flooding, terrain that would complicate the operation of a traditional excavator. Similarly, in the case that it is equipped with a large crane, the crane has the ability to operate on a variety of terrain, this aspect is ideal for construction jobs that have various types of working floors.

SIMILARITIES AND DIFFERENCES WITH A CONVENTIONAL EXCAVATOR
With respect to the structural plane, amphibious excavators have a design very similar to that of a conventional excavator, they can provide 360-degree turns while keeping the undercarriage fixed, they have an arm, boom, operating cabin, counterweight, etc. The specific difference lies in the undercarriage, which in the case of being an amphibious excavator is equipped with hulls or pontoons that resemble those of a boat to maximize traction and provide buoyancy to the equipment.
There are several types of amphibious excavators that are classified according to their way of displacement:
1.- The equipment used for use in shallow waters tends to move in a conventional way using only the undercarriage with pontoons, which reduces the pressure on the ground due to the width of the tracks and their greater contact surface, maximizing team traction.
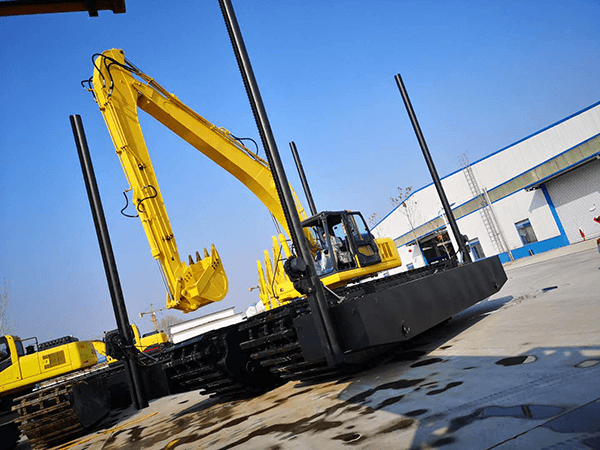
2.- Used for use in deep waters: They can be moved supported by the arm and boom of the excavator. To minimize the risk of overturning during operation, it is common to generally add an extra set of side pontoons, which include the so-called “spuds” or retention pillars, which are responsible for keeping the equipment in a zone. of specific work providing stability to the equipment because they improve the penetration to the ground.
3.-Used for use in deep waters supported by propellers: Their design is like that of equipment for deep waters, they are equipped with an additional set of pontoons, however, a propeller mechanism is implemented in the side hulls that will be the in charge of supporting the movement compared to that supported by the arm and boom.
OPTIONAL SUPPORT ELEMENTS
There are several accessories that enhance the abilities of amphibious excavators, among which the following options stand out:
1) OPTIONAL SPUD SYSTEM:
Additional side hydraulic spuds available that are used to improve the stability of the equipment in the work area, which are required if the water draft of the working condition of the site is 2 to 3.5 meters.
Spud, like its hydraulic mechanism built into the sealed vise pontoons, must be assembled on both sides of the amphibious excavator. The tip legs are controlled by hydraulic power for lying down and positioning. The length of the trowel legs is determined by the depth of the water in the work area. Before the excavator begins its production stage, you need to lift the tip legs and then turn on the hydraulic mechanism to insert the legs into the underwater mud. The Spud system is a great accessory because it greatly improves the underwater operational stability of the machine.

2) EXCAVATOR ACCESSORIES (BUCKETS, EXTENDED BOOMS)
1. EXTENDED BOOM
The extended boom is designed to meet the demand of large construction projects. The operating radius, height, and width of digging when using an extended boom increase the operating limit which serves to meet specific working conditions. Mainly the use of the extended boom does not represent any risk to the equipment, we can ensure the stability and safety of the work of the whole excavator by using an extended boom.
2. AMPHIBIOUS PONTOON
The amphibious pontoon is made of A36 steel, which is a special material for boats, and also of high-strength aluminum plate. Pontoons are shot blasted to make sure the surface is completely clean, free of contaminants and oxides. In addition, this process presents the steel with a surface texture that provides excellent adhesion of the first coat of paint, facilitating the painting process. Responsible structure design and finite element analysis of job site destructive testing greatly ensure that amphibious pontoons have adequate load capacity and safety.
3. TRACK CHAINS
The track chains and rollers of the amphibious pontoons are made of 40Cr, while the medium sleeves are made of a super wear-resistant material 20CrMnTi, due to this the sleeves have a high service life. The special three-track design will decrease the tension on each track and average the tension on the track shoes so that the track is more efficient. The main advantage is that the entire machine will have the ability to continue moving to the repair station after one of the chains breaks, which contributes significantly to reducing repair and maintenance costs during work. Also, all Amphibious Excavator Pontoon Track Chains have a rowing device, which can effectively improve the load capacity of the whole machine in the water.
4. CHAIN TENSIONER DEVICE
After the chains meet a reasonable wear time, which also depends on the operation, the chain pitch will be enlarged using the track pin, causing a slip or fall of the track. chain, which represents a great risk to work performance. The chain tensioning device will perform an adjustment of the chain wheel position to make sure that the chain pin and the drive gear have a perfect match to avoid problems. Bolt tensioning is the optimal configuration for the amphibious pontoon. In addition, there is an easier to maneuver tensioning system that you can employ: oil cylinder tensioning, with which the tensioning force can achieve a balance adjustment to make the entire operating system optimal, efficient, and safe.
5. RETRACTABLE PONTOON
This accessory provides greater autonomy to the operator. It means that the space of the 2 pontoons can be freely adjusted by the operating system within a certain range. There is a hydraulic control system on the connected beam of the two pontoons, which can be easily operated. In the case that the workspace in which to operate is a very narrow area, the pontoon space can be adjusted to a minimum while still operating normally. By flexibly adjusting the space between the pontoons, as a result, it can help to improve the stability of the chassis, as well as improve the overall work efficiency.












0 Comments