Table of Contents
There are several variables that determine the useful life of the undercarriage system, include most of the undercarriage parts. referring especially to the wear factor of the components or the assembly in general, in this article we will discuss the variables that can be controlled, among which the factors that stand out. they are specific to the equipment, in addition to the correct use of the excavator by the operator. The team’s own factors include variables such as track tension, component alignment, among other undercarriage parts.
FACTORS AFFECTING THE PRODUCTION OF THE UNDERCARRIAGE PARTS
CONTROLLABLE VARIABLES
FLOATATION
A track shoe width should be selected that provides adequate floatation, however, be careful not to exceed the width as this is also detrimental to the undercarriage. Controlling float will prevent the excavator from sinking to the ground.
PENETRATION-TRACTION
The extra width of the track shoe will not generate greater traction, the increase in production does not occur by choosing an adequate flotation.
MANEUVERABILITY
By using a wider track shoe, the excavator will be more difficult to handle because it is more difficult to make turns because the resistance is increased, therefore, this translates into a decrease in productivity.
VERSATILITY
By using a wider track shoe, it is possible to improve the versatility of the excavator in general, since it can work on “softer” terrain without losing flotation, however, the use of wider track shoes generates structural damage and causes an acceleration in wear.
USEFUL LIFE AND STRUCTURAL OF SYSTEM OF UNDERCARRIAGE
USEFUL LIFE OF THE TRACK SHOE
Using wider track shoes does not generate an increase in the useful life, it is more the additional material that is provided by using wider claws generates a greater wear, if the factor that is more relevant in the useful life of the track shoe is slippage.

STRUCTURAL LIFE OF TRACK SHOE
The width of the track shoe increases the bending stress, between the two there is a directly proportional relationship. Structurally increasing the width increases cracking, bending and the likelihood of loosening.
BASIC TIP FOR TRACK SHOE SELECTION
The narrowest possible track shoe should be selected, but one that provides adequate flotation and traction, without causing excessive undercarriage parts slip.
IDLER-ROLLER-TENSIONER SERVICE LIFE
When wider track shoes are used the wear, rate is higher on the sides of the link rail, on the flanges of the rollers and idlers, this occurs because there is more interference.
USEFUL LIFE OF THE PINS AND BUSHINGS
Depending on the increase in the width of the track shoe, there is an increase in the speed of wear of the external bushing in sealed and sealed / lubricated chains, in addition to the increase in internal wear that occurs in sealed chains, it occurs due to the increase in the loads, weight and torque.
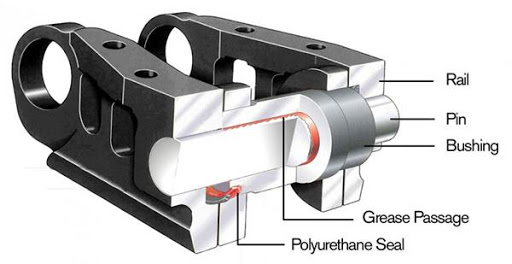
STRUCTURAL LIFE OF PINS AND BUSHINGS
In the case of using very wide track shoes in types of terrain with slopes or high impact, it could cause the pins and bushings to progressively loosen from the links, this loss of retention generates greater difficulty in turning.
SERVICE LIFE OF SEALED AND LUBRICATED CHAIN JOINTS
The most costly and relevant consequence of using track shoes that are too wide is the loss of lubricant and the estimated useful life of the seal, which results in unwanted drying out at the joints. Depending on the width of the track shoe and the force of the impact, the track link and the joint will be affected, that is, the greater these factors, the greater the probability that the joint will “open” and generate a loss of lubricant.
Loss of lubricant occurs as the bushing slides back and forth along the pin. The free space between the links, which is an opening, is called the “end game.” The “end play” can only be eliminated by exerting very strong pressure on the components when the undercarriage parts is pressed at the time of a track pressing job. To achieve optimization of lubricant and seal life, the excavator should use the narrowest possible track shoes with adequate flotation.
Proper alignment of the roller frame, idler, and sprocket is necessary to prevent accelerated and uneven wear on moving components within the undercarriage.
Performing a visual inspection, it should be followed as a rule that any difference between the left and right, inner, and outer and / or front and rear pattern can be caused by a misalignment of one or more undercarriage parts of the roller frame, sprockets and / or idler wheels.
VIBRATION
VIBRATION EXCITED BY THE TRACK
The most common vibration in these bulldozers is track-excited vibration. Due to the movement of the bulldozer, each track link, as part of a continuous rail, contacts curved surfaces, idlers, and track rollers. The contact between the rollers and track links generates greater wear in the central part of bulldozer track link. On the other hand, the contact between the chain rollers and the links generates wear at the ends where they intersect with the adjacent link. Wear is as a result; a saw pattern is formed on the surface of each of the track links.
In general, wear is accelerated by several factors, among which are considered relevant, abrasion, the moisture content of the ground, the weight of the entire excavator, the speed of movement and the operating conditions, especially the type of soil. Sometimes the excited vibration of the undercarriage parts does not seem to be very determining, this especially in the most uneven terrain, but it is quite relevant when working on a smooth surface.
The replacement of the insulation supports that are deteriorated is necessary, also the broken fasteners or to replace the missing ones, and a scheduled maintenance will reduce the vibration of the excavator. Other factors that can be modified are speed or operating technique.
GENERAL STATEMENTS ON ALIGNMENT PROBLEMS, SYMPTOMS, CAUSES, EFFECTS AND REMEDIES
- The probability of misalignment increases in direct proportion to the size and weight of the excavator, plus the impact factor that also contributes.
- Existing roller frame, idler and sprocket alignment problems will affect all track links in the same way.
- Roller frame, idler and sprocket alignment problems will unevenly affect chain rollers (front to rear rollers, inside to outside flanges, and inside and outside treads).
- The horizontal straightness of the roller frame will not affect the links but will affect the front and / or rear roller tracks compared to the center.
- Winding of the track will not cause damage close to the degree caused by misalignment.
- Carrier roll wear can be used as a visual indicator of roll frame alignment.
- Some alignment problems are temporary (caused by workloads). If both sides of a excavator have the same misalignment-type wear patterns, the cause may be flexing of the track roller frames due to workloads.
- If misalignment is suspected, it must be completely corrected before installing new components.
- Narrow chains increase the effect of all kinds of alignment problems by increasing loads between interfering components.
EXCAVATOR OPERATION

It must be clear that the life of the operator and his safety are the priorities when operating heavy machinery. Safe operation, especially to reduce the risks of tipping, involves understanding the excavator and the environmental conditions at the time of use.
There are many restrictions and prohibited uses that can affect rollover hazards including traveling and turning with very high implements and loads, etc. Some simple steps will be mentioned below, however, it is the operator’s responsibility to be alert to any equipment or environmental conditions that may jeopardize safe operation.
INITIATION
- You must be always with your vision on the excavator. Always use available handrails and steps and keep yourself well balanced. Do not grasp or hold any of the control levers and switches. Do not get on or off the moving excavator.
- Start and control the excavator only from the operator’s seat. The driver should not lean out of his seat when the engine is running.
- Before starting the engine, make sure the locking levers are in the “LOCKED” position and that all control levers and pedals are in neutral positions and that the seat belt is properly attached. Make sure that the control levers, jog lever, pedals and other control elements are not stuck and can be moved smoothly. If you notice that something is not in the indicated state, immediately identify the cause and correct it.
- Before operating the excavator, make sure the position of the bulldozer should be in front of you.
OPERATION
- Do not operate or start the engine in an unventilated area. Carbon monoxide gas is colorless, odorless, and deadly. If you experience low to moderate initial symptoms of co-poisoning, including the following symptoms: headache, fatigue, shortness of breath, nausea, or dizziness, seek medical attention immediately.
- Keep all safety excavator and covers in place. Replace damaged or missing safety devices before starting operation.
- When operating, keep your hands and body inside the wrap. Do not touch or press the control levers or pedals from outside the cab while the engine is running.
- Observe the following to avoid tipping:
- Do not operate on steep slopes.
- Do not swing the bucket downhill.
- Lower the dozer blade when digging.
- Keep the bucket as low as possible while driving uphill.
- Turn slowly on slopes (slow down a bit to do so).
- Do not place the excavator near the edges of ditches, as the earth may give way under the weight of the excavator.
- Never cross a slope horizontally or at an angle, as it may cause the machine to tip over.
- Avoid doing any work on theexcavator when it is on a slope, as it could throw it off balance and tip over.
05. Do not change course on steep slopes or the excavator could tip over.
06. When towing the excavator or pulling a load, the load must be less than the force of the tow line attached to the excavator.
07. The towing eye must not be used to tie down or lift the excavator.
08. When the excavator is parked on a slope, be sure to put the bucket on the ground and place all control levers in the neutral position. Keep other people away from the work area of the excavator. Be sure to lock the boom swing pedal when the boom swing function is not used.
ENDING
Park the excavator on a firm, flat and level surface. If this is not possible, park on the other side of the slope.
- Lower attachments and dozer blade to ground.
- Stop the engine.
- Relieve pressure in hydraulic system.
- Lock all control levers.
- Remove the key.
- Lock the cabin door.
IMPORTANT INFORMATION ON THE OPERATION OF THE EXCAVATOR
In any case, avoid the following operations:
- An excavation using the gravitational impact of the excavator.
- Compaction of gravel or soil using the bucket for compaction
- An excavation using the moving power of the excavator.
Do not try to drop or shake dirt adhering to the bucket: This can cause damage to the excavator. Adhered dirt can be shaken when the bucket is emptied by moving it out to full cylinder stroke. If this is not enough, move the stick as far as possible and operate the bucket back and forth.
Do not hit the dozer blade with the boom cylinder: Make sure the boom cylinder does not hit the dozer blade when digging deep. If necessary, rotate it so that the dozer blade is at the rear of the dozer.
Try to avoid collisions as much as possible: When moving the excavator, pay attention that the bulldozer does not collide with obstructions such as rocks, etc. Such collisions substantially shorten the life of the bulldozer and cylinder.
Support the Machine Correctly: When supporting the machine with the bulldozer, lower the bulldozer to engage the full width on the ground. If the water or mud level reaches higher than the tracks, the rotating bearing, rotating motor gear, and ring gear may be exposed to mud, water, and other foreign objects.
The excavator must be properly pressure washed after each use: especially the undercarriage parts area, this procedure can save you a lot of money because it prevents future breakdowns, if the operation has been carried out in greasy terrain it is recommended to use some type of detergent. Thoroughly clean the area around the ball joint bearing, rotary motor gear and crown to remove foreign objects.
Review Manual: It is recommended that you review the manufacturer’s manual for information on rotating bearing, rotating motor gear, and ring gear lubrication procedures.
Reinstall the protective cover.
Avoid overloading with the cylinders fully extended, as it will cause the machine to break down quickly.
Relieve residual hydraulic pressure immediately after engine has stopped.












0 Comments